Calibrating Audio Tones for MFJ TNCs: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
== Getting and installing Spectrogram == | == Getting and installing Spectrogram == | ||
The software we will be using is | The software we will be using is called Spectrogram. Earlier versions are freeware and will work with just about any flavor of Windows. We have only used it on Windows XP, but Windows 98, 2000 will likely work, possibly Vista and 7. | ||
You can download a copy of Spectrogram [http://ohiopacket.org/files/spectrogram/gram50.zip]here. | You can download a copy of Spectrogram here[http://ohiopacket.org/files/spectrogram/gram50.zip]. | ||
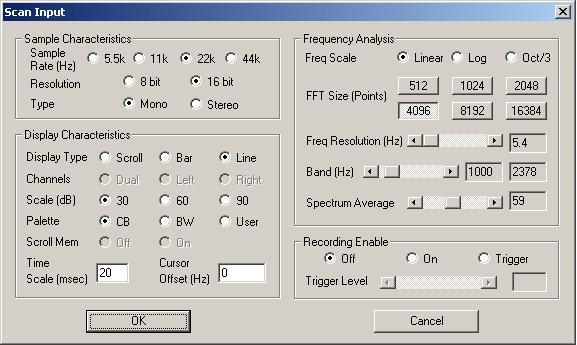
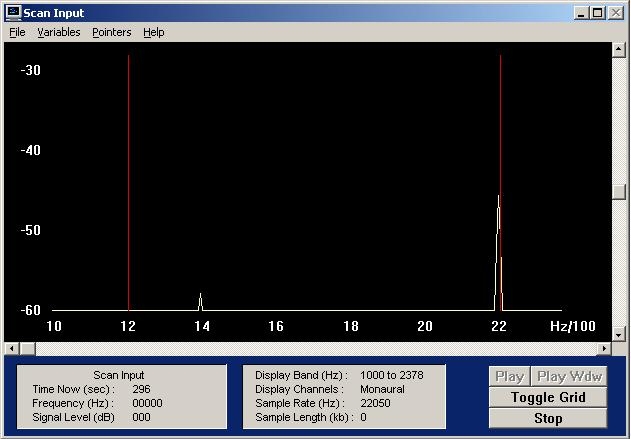
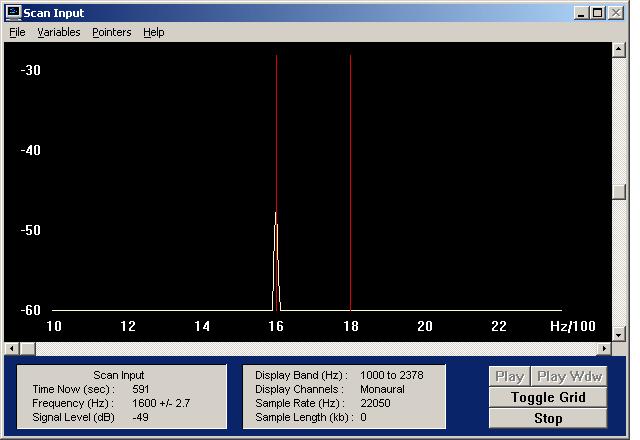
There is no installer for Spectrogram, so just unpack it to it's own folder and click on the "gram" executable. You will be prompted for Scan input settings. For the above purpose, we recommend starting with these: | |||
[[Image:Sg_input.jpg]] | |||
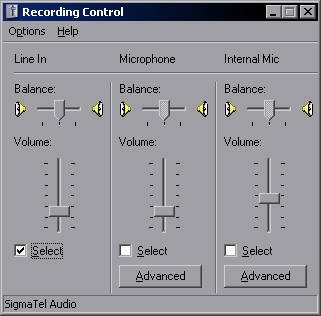
Once set, it is time to connect the TNC to the soundcard. Be sure you select the appropriate source (Line In or Microphone In), line in in this example. | |||
[[Image:sg_control.jpg]] | |||
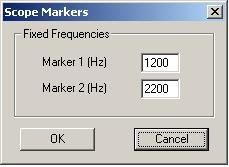
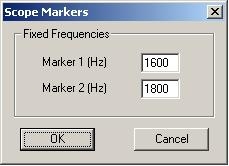
Lastly, set the markers for the target tones. For VHF, this can be set by selecting the Pointers menu at the top and selecting "Freq Mark" | |||
[[Image:sg_sm_vhf.jpg]] | |||
== Performing the Calibration == | |||
Next, it is time to set the TNC to be calibrated. It is assumed the factory eprom or standard TNC2 eprom are in use. After setting the terminal speed, parity and stop bits set properly, you will be given a cmd: prompt. From here, type "cali" | |||
'''cmd: cali'''<br> | |||
The TNC is now in calibration mode. While you have the top open, you may want to place a jumper (or one of the case screws across JMP4, which is towards the back, to the right side of the RS-232 connector. This will disable the hardware timeout timer. This is handy when calibrating tones and deviation, but should be removed for normal operations. Now, type "K", this should send the TNC into transmit mode, with proper input channel selected and cables connected, a small peak should appear across the screen. In this example, this is an MFJ-1274 being tuned. | |||
[[Image:sg_high_vhf_off.jpg]] | |||
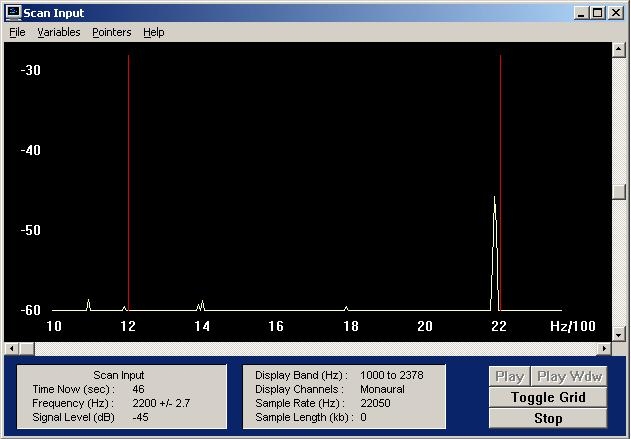
You will notice along the bottom of the Spectogram window is the frequency of the cursor/crosshair. This is absent from the screen captures, but once Spectrogram is running, they will be visible. Try to center the crosshairs as close to the target freqency as possible. With a slight adjustment to R77, the tone is now centered on 2200Hz. | |||
[[Image:sg_high_vhf-set.jpg]] | |||
Now hit the space bar on the keyboard to toggle down to the low tone. Adjust R78 appropriately to target 1200Hz. | |||
The same steps can be repeated for HF calibration, simply press the HF switch on the back, change the Pointers -> Freq Mark to 1600 and 1800 Hz | |||
[[Image:sg_sm_hf.jpg]] | |||
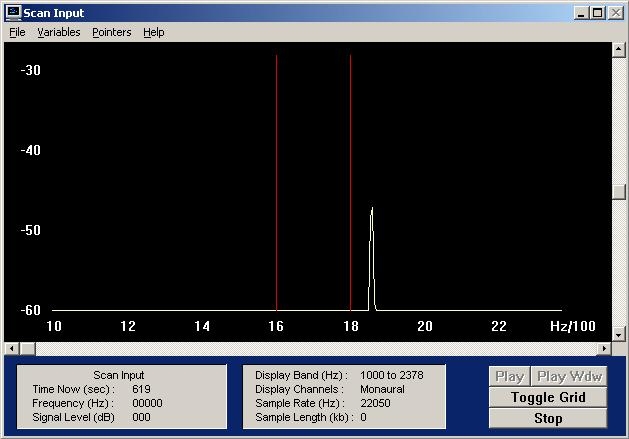
Here is a miscalibrated HF high tone 1800 Hz | |||
[[Image:sg_high_hf_off.jpg]] | |||
And a correctly tuned tone via R105. | |||
[[Image:sg_high_hf_set.jpg]] | |||
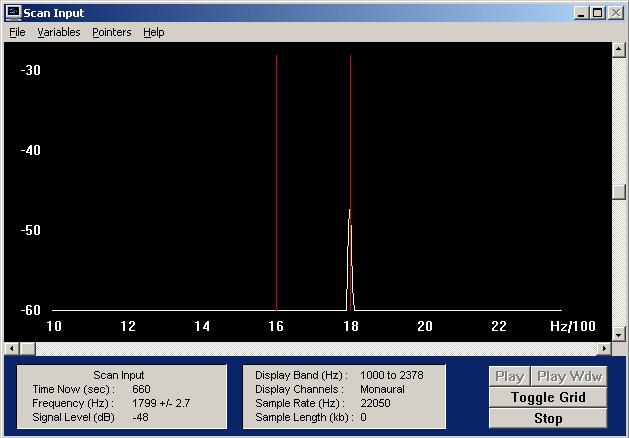
And a properly calibrated low tone 1600 Hz | |||
[[Image:sg_low_hf_set.jpg]] | |||
Once finished, you can hit "K" to stop sending tones, then "Q" to return to the cmd: prompt. | |||
---- | |||
There are a few issues that may need to be addressed to get proper tuning setup. First, when putting the TNC into calibration mode and sending a tone, it is possible that no tone markers will appear on the screen. If this is the case, try adjusting the audio mixer within Windows to bring the level up to where it is visible. If that does not work, you can adjust the deviation potentiometer to provide adequate drive level for the PC to pickup the tones. Keep in mind that once tones are properly calibrated, the deviation should be recalibrated as well. For 1200 Baud, target deviation should be set near 3.25-3.5 KHz. | |||
Latest revision as of 13:46, 16 April 2010
Properly calibrating audio tones on a TNC can make a huge difference when it comes to efficiency of a packet link. While some TNCs do not need nor allow calibration, the "workhorse" of most packet networks do. The MFJ-1270b, 1270c, 1274 and 1276 radios offer both 1200 and 300 baud operation as well as optional modems to run at 2400, 4800 or 9600 baud. We will only discuss 1200 and 300 baud here, but the same principles should apply to any speed.
Connecting the TNC to your computer
The procedures outlined here only apply to select few TNCs. With proper documentation of the TNC, these should be applicable to any TNC where you can monitor their audio out. For the MFJ TNC2 clones, there is a 1/8" mono jack in the back of the TNC. This means a simple mono (or stereo) audio jumper cable between the TNC and the Line In or Microphone in will suffice. For others, one could wire up a connector to fit the TNC, sending TXA to the left channel (tip) and ground to the shaft of a standard 1/8" mono plug suitable to plug into a computer soundcard.
The MFJ-1270B and MFJ-1274
The MFJ-1270B and MFJ-1274 are nearly identical on the inside with the exception of the tuning indicator on the front of the MFJ-1274. The tuning procedure for both are identical. To start, open up the TNC, they have 4 screws total holding the cover on. A small phillips screwdriver works nicely. You will want to locate a small standard screwdriver or non-metallic tuning tool to actually adjust the potentiometers which govern audio tone.
Once the cover is removed, with the TNC facing you, you will see 4 sets of potentiometers bundled together in the center, then 2 more off to the left.
In the center you will find
R79 - Receive Audio Level
R78 - Low tone VHF (should be 1200 Hz)
R77 - High tone VHF (should be 2200 Hz)
R76 - Transmit audio
The 2 off to the left are
R106 - Low tone HF (should be 1600 Hz)
R105 - High tone HF (should be 1800 Hz)
The MFJ-1270C and MFJ-1276
Much like their predecessors, the MFJ-1270C and MFJ-1276 are nearly identical as well. The primary difference being that the recieve and transmit level potentiometers are located on the left side of the board with small holes in the cover to allow their adjustment without removing the cover. Similarly to the 1270B/1274, in the center you will find:
R79 - Audio Level in VHF
R78 - Low Tone VHF (should be 1200 Hz)
R77 - High Tone VHF (should be 2200 Hz)
R113 - Audio Level in HF
The two off to the left are
R106 - Low tone HF (should be 1600 Hz, though the manual says 2125 Hz)
R105 - Low tone HF (should be 1800 Hz, though the manual says 2275 Hz)
The discrepancy of tones for HF on the MFJ-1270C/1276 is just to have one standard. In our experience, the 1600/1800Hz mark/space tones are the most common and generally make HF connections easier.
Getting and installing Spectrogram
The software we will be using is called Spectrogram. Earlier versions are freeware and will work with just about any flavor of Windows. We have only used it on Windows XP, but Windows 98, 2000 will likely work, possibly Vista and 7.
You can download a copy of Spectrogram here[1].
There is no installer for Spectrogram, so just unpack it to it's own folder and click on the "gram" executable. You will be prompted for Scan input settings. For the above purpose, we recommend starting with these:
Once set, it is time to connect the TNC to the soundcard. Be sure you select the appropriate source (Line In or Microphone In), line in in this example.
Lastly, set the markers for the target tones. For VHF, this can be set by selecting the Pointers menu at the top and selecting "Freq Mark"
Performing the Calibration
Next, it is time to set the TNC to be calibrated. It is assumed the factory eprom or standard TNC2 eprom are in use. After setting the terminal speed, parity and stop bits set properly, you will be given a cmd: prompt. From here, type "cali"
cmd: cali
The TNC is now in calibration mode. While you have the top open, you may want to place a jumper (or one of the case screws across JMP4, which is towards the back, to the right side of the RS-232 connector. This will disable the hardware timeout timer. This is handy when calibrating tones and deviation, but should be removed for normal operations. Now, type "K", this should send the TNC into transmit mode, with proper input channel selected and cables connected, a small peak should appear across the screen. In this example, this is an MFJ-1274 being tuned.
You will notice along the bottom of the Spectogram window is the frequency of the cursor/crosshair. This is absent from the screen captures, but once Spectrogram is running, they will be visible. Try to center the crosshairs as close to the target freqency as possible. With a slight adjustment to R77, the tone is now centered on 2200Hz.
Now hit the space bar on the keyboard to toggle down to the low tone. Adjust R78 appropriately to target 1200Hz.
The same steps can be repeated for HF calibration, simply press the HF switch on the back, change the Pointers -> Freq Mark to 1600 and 1800 Hz
Here is a miscalibrated HF high tone 1800 Hz
And a correctly tuned tone via R105.
And a properly calibrated low tone 1600 Hz
Once finished, you can hit "K" to stop sending tones, then "Q" to return to the cmd: prompt.
There are a few issues that may need to be addressed to get proper tuning setup. First, when putting the TNC into calibration mode and sending a tone, it is possible that no tone markers will appear on the screen. If this is the case, try adjusting the audio mixer within Windows to bring the level up to where it is visible. If that does not work, you can adjust the deviation potentiometer to provide adequate drive level for the PC to pickup the tones. Keep in mind that once tones are properly calibrated, the deviation should be recalibrated as well. For 1200 Baud, target deviation should be set near 3.25-3.5 KHz.